Unbeknownst to many, foot fungus and bacterial infections can lurk in the most unexpected places, causing discomfort and affecting overall foot health. Understanding the different types of foot fungus and bacterial infections is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the various types of foot fungus and bacterial infections, shedding light on their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
1. Athlete’s Foot: The Common Fungal Culprit
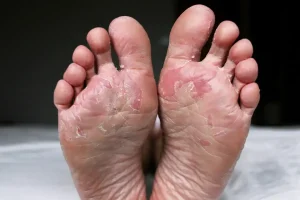
Athlete’s foot, also known as tinea pedis, is one of the most common types of foot fungus infections. It thrives in warm, moist environments, making it prevalent among athletes and individuals who wear tight-fitting shoes for prolonged periods. Symptoms of athlete’s foot include itching, burning, redness, and cracking of the skin, particularly between the toes. Without proper treatment, athlete’s foot can spread to other areas of the foot or to other individuals through direct contact.
2. Toenail Fungus: A Stubborn Fungal Infection
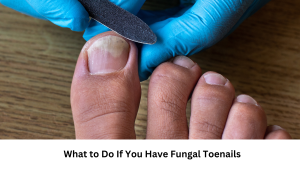
Toenail fungus, or onychomycosis, is a fungal infection that affects the toenails, causing them to become thickened, discolored, and brittle. This type of foot fungus can be challenging to treat due to its location beneath the nail surface. It often develops as a result of untreated athlete’s foot or prolonged exposure to warm, damp environments. Without intervention from a podiatrist, toenail fungus can worsen over time and lead to complications such as nail deformity or secondary bacterial infections.
3. Ringworm: Not Just for Children
Ringworm, or tinea corporis, is a fungal infection that can affect the feet, as well as other parts of the body. Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by worms but rather by a group of fungi known as dermatophytes. On the feet, ringworm presents as red, scaly patches that may be itchy or uncomfortable. Prompt treatment with antifungal medication is essential to prevent the spread of ringworm and alleviate symptoms.
4. Bacterial Infections: The Other Side of the Coin
While foot fungus infections often steal the spotlight, bacterial infections are equally significant concerns for foot health. Bacterial infections can occur as a result of breaks in the skin, such as cuts, scrapes, or puncture wounds, allowing bacteria to enter and multiply. Symptoms of bacterial infections may include redness, swelling, warmth, and drainage from the affected area. In severe cases, bacterial infections can lead to cellulitis or even sepsis if left untreated.
5. Cellulitis: A Serious Bacterial Infection
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin and underlying tissues that can affect the feet and lower legs. It typically presents as redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected area. In severe cases, cellulitis may be accompanied by fever, chills, and systemic symptoms. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is crucial to prevent the spread of infection and reduce the risk of complications such as abscess formation or bloodstream infection.
6. Plantar Warts: A Viral Affliction
Plantar warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and can occur on the soles of the feet. These small, rough growths may be mistaken for calluses or corns but are actually caused by viral infection. Plantar warts can be painful, especially when walking or standing, and may require treatment by a podiatrist to resolve. Over-the-counter wart treatments are generally ineffective for plantar warts and may cause irritation or damage to the surrounding skin.
7. Diabetic Foot Infections: A Complication of Diabetes
Individuals with diabetes are at increased risk of developing foot infections due to nerve damage, poor circulation, and compromised immune function. Diabetic foot infections can range from mild to severe and may lead to complications such as ulcers, gangrene, or limb amputation if not properly treated. Proper foot care, including daily inspection, moisturizing, and wearing properly fitting shoes, is essential for individuals with diabetes to prevent foot infections and maintain overall foot health.
8. Prevention and Treatment: Consulting a Podiatrist
Preventing and treating foot fungus and bacterial infections often requires the expertise of a podiatrist. A podiatrist can provide personalized treatment recommendations based on the specific type of infection, its severity, and any underlying medical conditions. Treatment options may include topical or oral antifungal medications, debridement of infected tissue, laser therapy, or surgical intervention for severe cases. Additionally, a podiatrist can offer guidance on preventive measures, such as proper foot hygiene, wearing breathable footwear, and avoiding shared public spaces barefoot.
Conclusion: Taking Steps Towards Healthy Feet
By understanding the various types of foot fungus and bacterial infections, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their feet and maintain overall foot health. From practicing good foot hygiene to seeking prompt treatment for infections, prioritizing foot care is essential for preventing complications and enjoying a life free from foot discomfort and pain.