Plantar Fasciitis Diagnose and Treatment
At Michigan Avenue Podiatry, we understand the debilitating impact of plantar fasciitis on your daily life. Our comprehensive approach to plantar fasciitis treatment is designed to alleviate pain, promote healing, and restore mobility so you can get back to doing what you love.
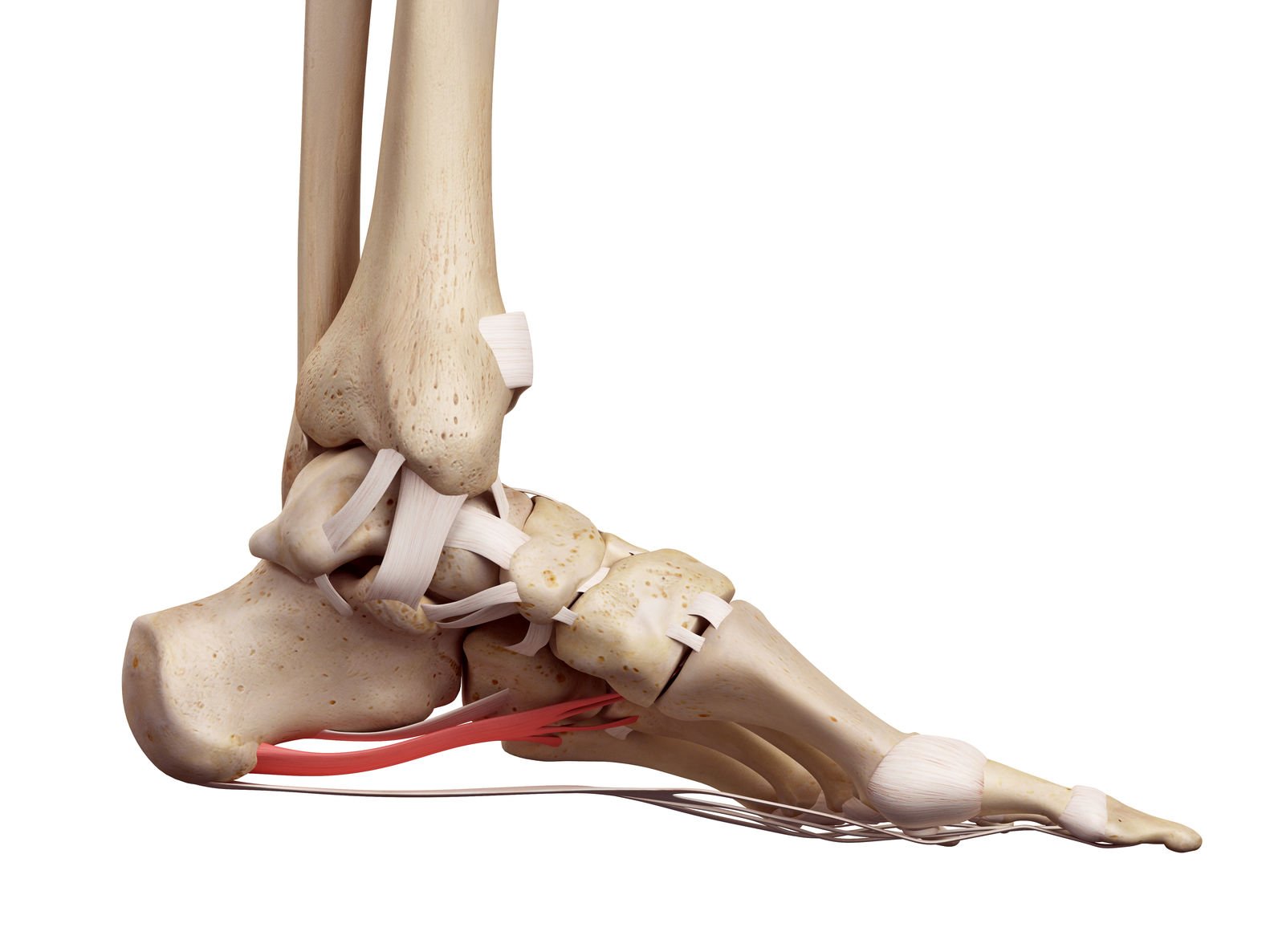
What is Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This inflammation can result in stabbing pain near the heel, especially with the first steps in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest.
Our Approach to Treatment
1. Personalized Evaluation
We begin with a thorough examination to assess the extent of your condition and identify any contributing factors. Understanding your unique biomechanics and lifestyle helps us tailor a treatment plan that addresses your specific needs.
2. Conservative Therapies
Our treatment approach emphasizes conservative methods to relieve pain and promote healing without the need for invasive procedures whenever possible. These may include:
- Orthotic Devices: Custom orthotic inserts can provide support and redistribute pressure, reducing strain on the plantar fascia.
- Stretching Exercises: Targeted stretching routines can help alleviate tightness in the calf muscles and plantar fascia, improving flexibility and reducing pain.
- Physical Therapy: Guided exercises and therapeutic techniques can strengthen the foot muscles, enhance stability, and improve overall function.
- Night Splints: Wearing night splints can help maintain a gentle stretch on the plantar fascia while you sleep, reducing morning pain and stiffness.
3. Advanced Treatments
For cases that do not respond adequately to conservative measures, we offer advanced treatment options to expedite healing and provide long-lasting relief:
- Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT): ESWT delivers shockwaves to the affected area, stimulating blood flow and promoting tissue repair.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP injections harness the healing properties of your own blood to accelerate tissue regeneration and reduce inflammation.
- Tenex Procedure: This minimally invasive technique uses ultrasonic energy to remove damaged tissue, allowing for quicker recovery and symptom relief.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
We provide guidance on lifestyle modifications and preventive measures to minimize the risk of recurrent plantar fasciitis. This may include footwear recommendations, activity modifications, and strategies to maintain healthy foot mechanics.
Your Path to Relief Starts Here
Don’t let plantar fasciitis hold you back from enjoying life to the fullest. At Michigan Avenue Podiatry,, we’re dedicated to helping you overcome foot pain and regain mobility. Schedule a consultation today to take the first step towards lasting relief and a healthier, happier you.
