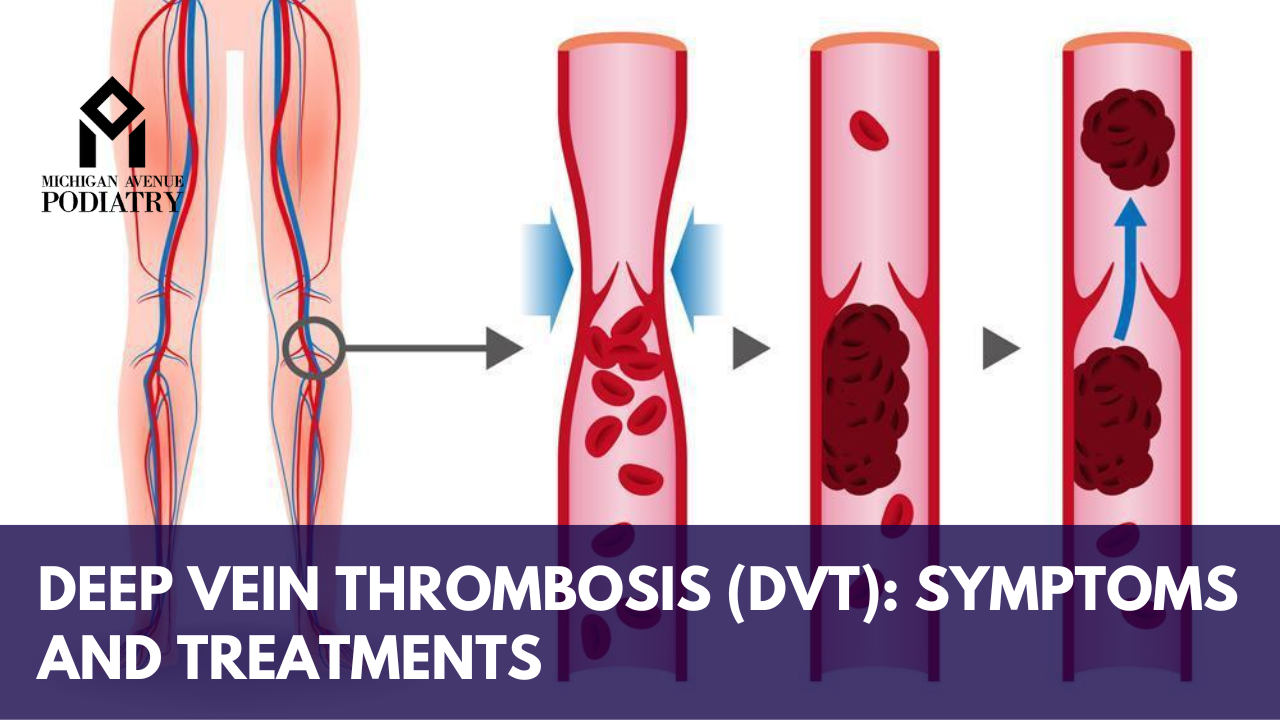
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in the deep veins of the body, typically in the legs. If left untreated, DVT can lead to potentially life-threatening complications such as pulmonary embolism. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options for DVT, with insights from podiatrist experts and foot doctors.
Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis Symptoms:
- Leg Pain and Swelling: One of the most common symptoms of DVT is persistent pain and swelling in the affected leg, typically occurring in the calf or thigh. The affected area may feel tender to the touch, warm, or visibly swollen.
- Redness and Warmth: In addition to pain and swelling, individuals with DVT may notice redness or discoloration of the skin over the affected vein. The skin may feel warm to the touch due to inflammation.
- Leg Fatigue and Heaviness: Some individuals with DVT may experience a sense of fatigue or heaviness in the affected leg, especially with prolonged standing or walking. This sensation may worsen over time as the clot grows larger.
- Visible Veins: In severe cases of DVT, the affected vein may become visibly distended or enlarged, appearing as a rope-like bulge beneath the skin. This is known as superficial thrombophlebitis.
- Complications: If a blood clot breaks loose from the vein and travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism, which can be life-threatening. Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include chest pain, shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, and coughing up blood.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for DVT:
- Medical Evaluation: If DVT is suspected, a healthcare provider will conduct a physical examination and may order diagnostic tests such as ultrasound imaging, blood tests, or venography to confirm the diagnosis.
- Anticoagulant Medications: The primary treatment for DVT involves anticoagulant medications, also known as blood thinners, to prevent further blood clot formation and reduce the risk of complications. Commonly prescribed anticoagulants include heparin, warfarin, and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs).
- Compression Therapy: Wearing compression stockings or bandages can help improve blood flow in the legs and reduce swelling associated with DVT. These garments apply gentle pressure to the veins, preventing blood from pooling and reducing the risk of clot formation.
- Thrombolytic Therapy: In severe cases of DVT, thrombolytic therapy may be used to dissolve the blood clot quickly. This treatment involves administering clot-dissolving medications directly into the affected vein.
- Surgical Intervention: In rare cases, surgical procedures such as thrombectomy or vena cava filter placement may be necessary to remove or prevent the spread of blood clots in individuals with DVT.
Prevention Strategies for DVT:
- Stay Active: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can help improve circulation and reduce the risk of DVT. Avoid prolonged periods of immobility, especially during long flights or car rides.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a risk factor for DVT, so maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can help reduce the risk of blood clot formation.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption can increase the risk of DVT, so it’s important to quit smoking and drink alcohol in moderation.
- Wear Compression Stockings: If you’re at increased risk of DVT due to surgery or prolonged immobility, wearing compression stockings can help improve blood flow in the legs and reduce the risk of blood clot formation.
Conclusion: Deep Vein Thrombosis is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent potentially life-threatening complications. By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options for DVT, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and maintain optimal vascular health. Consultation with podiatrist experts and foot doctors can provide personalized guidance and support in managing DVT and promoting overall well-being.
To schedule an appointment with our board-certified foot and ankle specialists, Book Your Appointment Now