For individuals grappling with persistent heel pain caused by plantar fasciitis, traditional treatments may offer temporary relief but often fall short of providing long-term solutions. However, advancements in podiatric medicine have paved the way for minimally invasive procedures like Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy (EPF) surgery, offering hope for those seeking lasting relief. Let’s delve deeper into this innovative surgical approach, exploring its efficacy, recovery process, and potential benefits.
Understanding Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy:
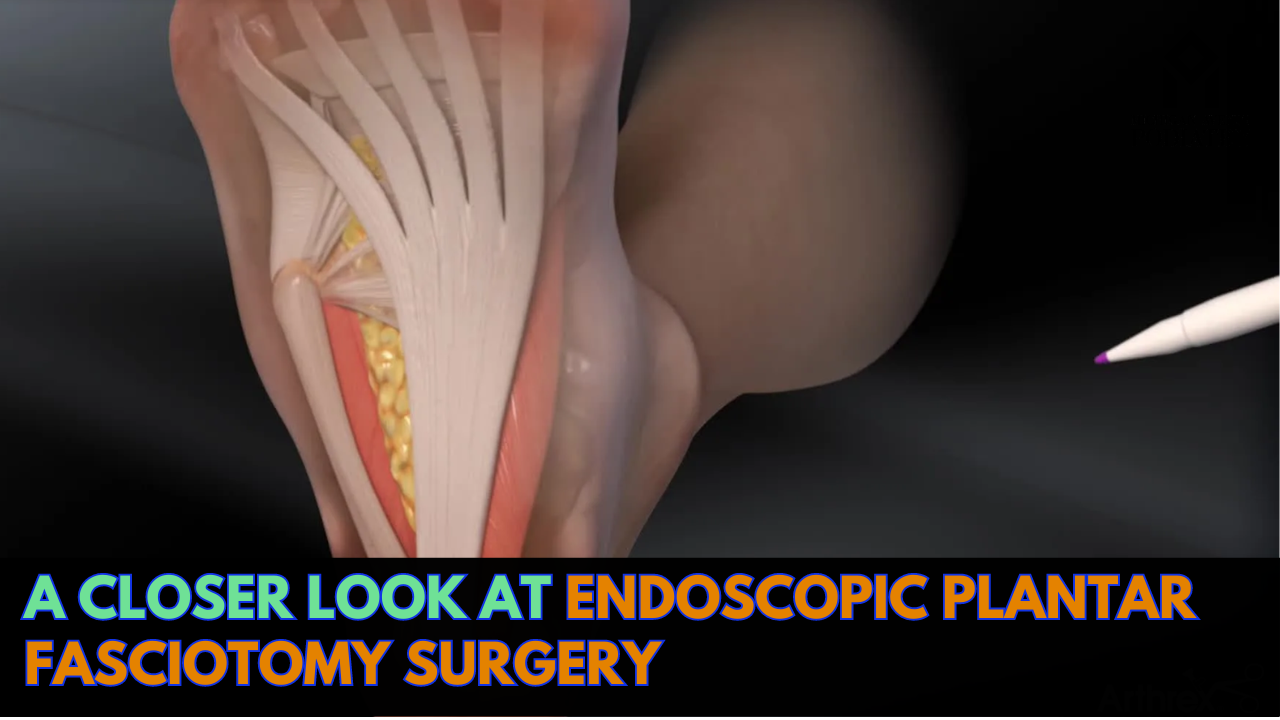
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure designed to alleviate heel pain by releasing tension in the plantar fascia, a band of tissue connecting the heel bone to the toes. Unlike traditional open surgery, which involves larger incisions and longer recovery times, EPF utilizes small incisions and a tiny camera (endoscope) to guide the surgeon’s movements with precision.
The Procedure in Detail:
During an Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy, the surgeon makes two small incisions—one near the heel and another near the ball of the foot. Through these incisions, the endoscope and specialized surgical instruments are inserted to access the plantar fascia. The surgeon then carefully severs the tight or damaged portion of the fascia, relieving pressure and allowing the foot to regain its natural range of motion.
Benefits of Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Surgery:
- Minimally Invasive: Compared to traditional open surgery, EPF involves smaller incisions, resulting in less tissue damage, reduced scarring, and a lower risk of complications such as infection.
- Faster Recovery: The minimally invasive nature of EPF typically translates to shorter recovery times, allowing patients to return to their normal activities sooner compared to traditional surgical methods.
- Precision and Accuracy: With the aid of an endoscope, surgeons can visualize the internal structures of the foot with enhanced clarity, ensuring precise incision placement and targeted treatment of the affected area.
- Reduced Pain: By releasing tension in the plantar fascia, EPF aims to alleviate heel pain and discomfort, enabling patients to experience improved mobility and quality of life.
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Recovery:
Following Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy surgery, patients are usually advised to rest and elevate the affected foot to minimize swelling and discomfort. Depending on the individual’s condition and the extent of the procedure, weight-bearing activities may be gradually reintroduced under the guidance of a podiatrist or healthcare provider.
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Recovery Time:
While recovery times can vary from person to person, many patients report significant improvement in symptoms within a few weeks post-surgery. Full recovery may take several months, during which physical therapy exercises and supportive footwear may be recommended to optimize healing and prevent recurrence of symptoms.
Conclusion:
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy surgery represents a promising option for individuals struggling with chronic heel pain due to plantar fasciitis. By offering a minimally invasive approach with potential benefits such as faster recovery times and reduced postoperative discomfort, EPF holds the promise of restoring mobility and enhancing quality of life for those in need. If you’re considering EPF surgery as a treatment option, consult with a qualified podiatrist to discuss your individual needs and determine the best course of action.