Ingrown toenails are a common foot ailment that can cause discomfort, pain, and even infection if left untreated. From understanding the underlying causes to exploring treatment options, this comprehensive blog post aims to provide valuable insights into ingrown toenails, along with expert guidance from podiatrists.
Understanding Ingrown Toenails:
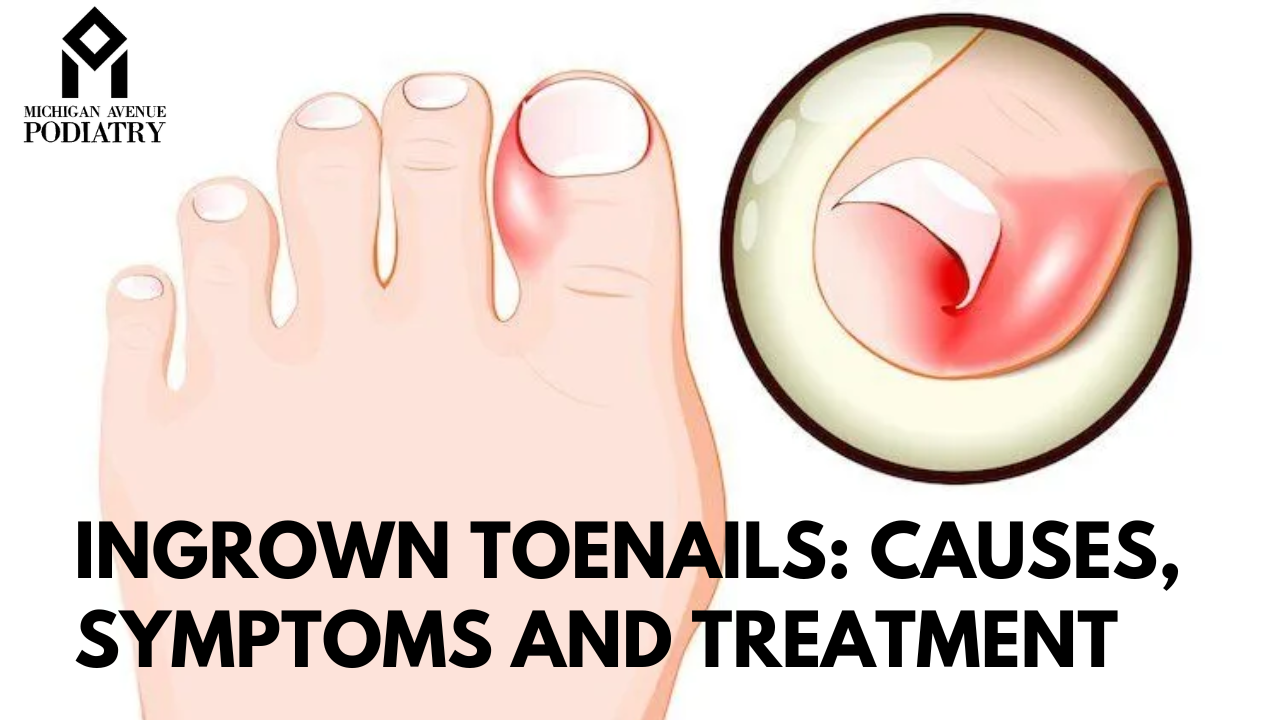
- What Are Ingrown Toenails? Ingrown toenails occur when the edge of the toenail grows into the surrounding skin, leading to pain, inflammation, and potential infection. This condition typically affects the big toe but can occur in any toe.
- Causes of Ingrown Toenails: Several factors can contribute to the development of ingrown toenails, including:
- Improper nail trimming: Cutting nails too short or rounding the edges can encourage ingrown toenails.
- Tight footwear: Wearing shoes that crowd the toes can exert pressure on the nails, increasing the risk of ingrowth.
- Trauma: Stubbing the toe or repetitive trauma to the nail can cause it to grow improperly.
- Genetics: Some individuals may inherit a predisposition to ingrown toenails due to the shape or structure of their nails.
- Symptoms of Ingrown Toenails: Common symptoms of ingrown toenails include:
- Pain and tenderness along the edge of the nail
- Redness and swelling around the affected toe
- Increased sensitivity to pressure or touch
- Pus or drainage if the ingrown nail becomes infected
- Complications of Infected Ingrown Toenails: If left untreated, ingrown toenails can lead to complications such as:
- Infection: Bacterial infection can occur, causing pain, swelling, and discharge.
- Abscess formation: Pus-filled pockets may develop around the ingrown nail, requiring drainage.
- Chronic inflammation: Recurrent ingrown toenails can lead to chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
Treatment Options:
- Conservative Measures:
- Soaking the affected foot in warm, soapy water can help soften the nail and reduce inflammation.
- Gentle nail trimming: Cutting the nail straight across and avoiding sharp corners can prevent ingrowth.
- Wearing properly fitting footwear with ample toe room can alleviate pressure on the toenails.
- Professional Intervention:
- Podiatrists offer various treatments for ingrown toenails, including:
- Partial nail avulsion: Surgical removal of the ingrown portion of the nail to promote healing.
- Nail lifting: Lifting the ingrown nail edge and placing a small wedge to prevent regrowth into the skin.
- Antibiotics: If the ingrown toenail is infected, oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed to clear the infection.
- Podiatrists offer various treatments for ingrown toenails, including:
Expert Podiatrist Insights: Podiatrists play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating ingrown toenails, offering personalized care tailored to each patient’s needs. They can provide expert guidance on prevention strategies and recommend appropriate interventions to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Conclusion: Ingrown toenails are a common foot problem that can cause significant discomfort and inconvenience if not addressed promptly. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ingrown toenails, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy feet and seek timely intervention from a podiatrist when needed. Don’t let ingrown toenails disrupt your daily life—consult a podiatrist for expert care and guidance.
FAQs on Ingrown Toenails
What causes ingrown toenails?
Ingrown toenails occur when the edge of a toenail grows into the surrounding skin. This condition can be caused by several factors, including:
- Improper Toenail Trimming: Cutting toenails too short or rounding the edges can encourage the nail to grow into the skin.
- Tight Footwear: Wearing shoes that squeeze the toes together can increase pressure on the toenails, leading to ingrowth.
- Injury: Trauma to the toenail, such as stubbing your toe or dropping something heavy on it, can cause the nail to grow incorrectly.
- Genetics: Some people inherit a tendency for curved or thick toenails, which are more prone to becoming ingrown.
- Poor Foot Hygiene: Keeping feet clean and dry can prevent infections and other conditions that might lead to ingrown toenails.
How to treat ingrown toenails?
Treating ingrown toenails often involves both home remedies and professional medical interventions, depending on the severity of the condition:
- Warm Soaks: Soak the affected foot in warm, soapy water several times a day to reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Proper Nail Trimming: Trim toenails straight across and avoid cutting them too short. Use clean, sharp nail clippers.
- Wear Comfortable Shoes: Opt for shoes with plenty of toe room to avoid further pressure on the toenails.
- Antibiotic Ointment: Apply an over-the-counter antibiotic ointment to prevent infection.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage discomfort.
- Consult a Podiatrist: For severe or persistent cases, see a podiatrist. They may perform minor surgical procedures, such as partial nail removal, to correct the issue.
What do ingrown toenails look like?
Ingrown toenails can vary in appearance, but common signs include:
- Redness: The skin around the ingrown nail is often red and inflamed.
- Swelling: The affected area may swell and become tender to the touch.
- Pain: Pain is usually felt along the edges of the toenail, particularly when pressure is applied.
- Pus: If the ingrown toenail becomes infected, pus may be visible around the nail.
- Overgrowth of Skin: Sometimes, the skin around the ingrown nail grows over it, making the condition more painful and difficult to treat.