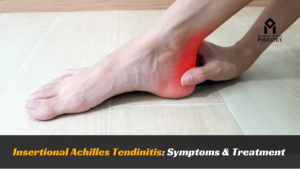
Achilles tendonitis is a common yet debilitating condition that affects many individuals, particularly athletes and active individuals. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for effectively managing this condition and returning to an active lifestyle.
Achilles Tendonitis Treatment Strategies
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Symptoms of Achilles tendonitis often manifest as pain, stiffness, swelling, and tenderness along the back of the leg or above the heel. If left untreated, it can lead to further complications such as Achilles tendon rupture. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination by a qualified podiatrist, along with imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI.
Conservative Treatment Approaches:
The initial treatment for Achilles tendonitis usually involves conservative approaches aimed at reducing pain and inflammation. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are commonly recommended, along with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to alleviate discomfort. Additionally, physical therapy plays a crucial role in rehabilitating the tendon and preventing future injuries.
Achilles Tendonitis Treatment Exercises:
Incorporating specific exercises into your treatment regimen can help strengthen the Achilles tendon and surrounding muscles, promoting healing and preventing re-injury. Eccentric exercises, calf stretches, and towel stretches are among the most effective exercises for Achilles tendonitis treatment. Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of these exercises is key to achieving optimal results.
Physical Therapy Intervention:
Physical therapy plays a central role in the comprehensive treatment of Achilles tendonitis. Skilled physical therapists utilize various modalities and techniques to improve flexibility, strength, and mobility in the affected tendon. Hands-on therapies, such as massage and manual manipulation, can also aid in reducing tension and promoting healing.
Advanced Treatment Options:
For cases of chronic Achilles tendonitis or severe pain, advanced treatment options may be necessary. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, and ultrasound-guided interventions are among the innovative therapies available to accelerate healing and alleviate symptoms. However, these treatments should be administered under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
Surgical Intervention:
In rare cases where conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgical procedures for Achilles tendonitis typically involve debridement of damaged tissue, tendon repair, or lengthening procedures. A thorough evaluation by an orthopedic surgeon or podiatric specialist is essential to determine the most appropriate surgical approach.
Rehabilitation and Recovery:
Following surgical intervention or prolonged conservative treatment, a structured rehabilitation program is crucial for ensuring a successful recovery. Gradually reintroducing weight-bearing activities, functional exercises, and sports-specific training helps rebuild strength and endurance while minimizing the risk of re-injury. Close collaboration between the patient, physical therapist, and healthcare provider is essential throughout the rehabilitation process.
Conclusion:
Achilles tendonitis can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, but with timely intervention and comprehensive treatment strategies, it can be effectively managed. From conservative measures to advanced therapies and surgical options, there are various approaches available to address this challenging condition. By working closely with a multidisciplinary healthcare team, individuals can overcome Achilles tendonitis and return to the activities they love.