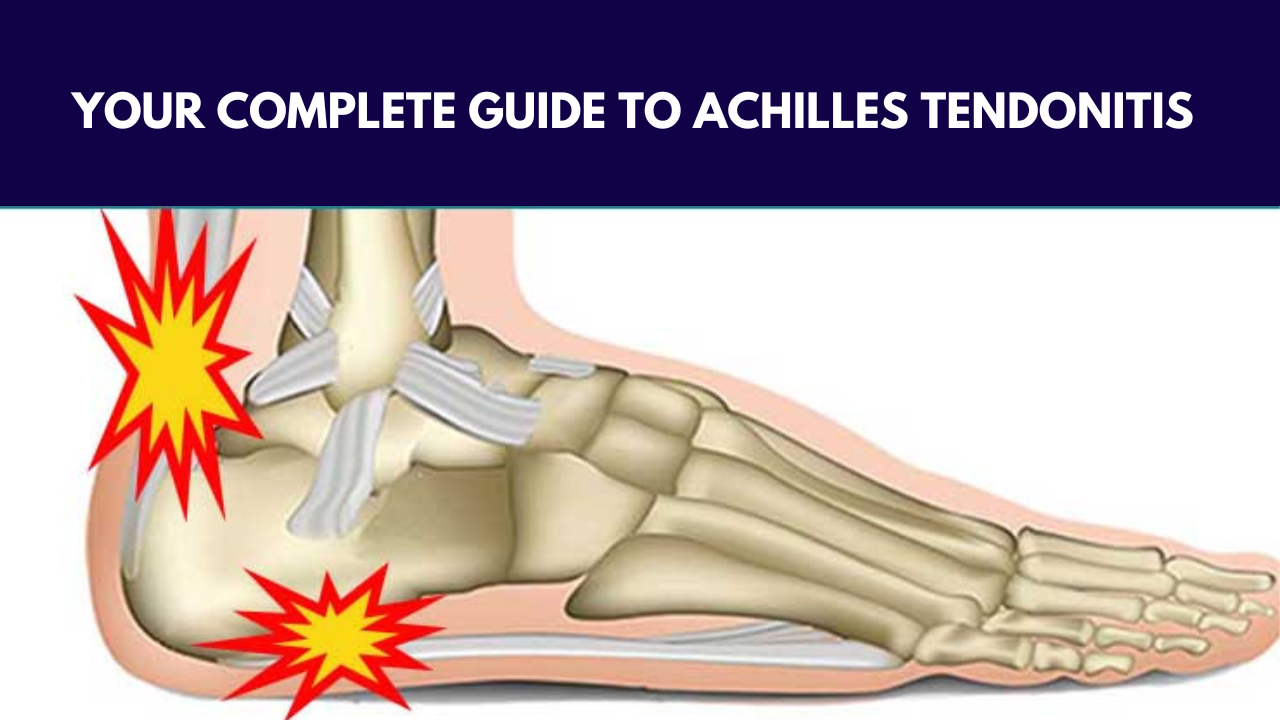
Achilles tendonitis is a common condition that affects the Achilles tendon, the largest tendon in the body. This vital structure connects the calf muscles to the heel bone and plays a crucial role in various activities such as walking, running, and jumping. However, overuse, improper footwear, sudden increases in physical activity, or biomechanical issues can lead to inflammation and irritation of the Achilles tendon, resulting in Achilles tendonitis. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies for Achilles tendonitis, empowering you with the knowledge to manage and overcome this debilitating condition.
Understanding Achilles Tendonitis:
Achilles tendonitis is characterized by pain, swelling, and stiffness in the Achilles tendon, particularly near the heel. It often develops gradually over time as a result of repetitive stress or strain on the tendon. Athletes and individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive jumping or running are at a higher risk of developing Achilles tendonitis. Additionally, factors such as tight calf muscles, improper footwear, poor biomechanics, and sudden increases in training intensity can contribute to the development of this condition.
Symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis:
The hallmark symptoms of Achilles tendonitis include:
- Pain and stiffness: Pain and stiffness in the Achilles tendon, particularly during physical activity or upon waking up in the morning.
- Swelling: Swelling and tenderness along the length of the Achilles tendon, especially near the heel.
- Reduced range of motion: Difficulty flexing the foot or pointing the toes downward due to tightness and inflammation of the tendon.
- Bony growth: In some cases, chronic Achilles tendonitis may lead to the formation of a bony bump at the back of the heel known as Haglund’s deformity.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Achilles Tendonitis:
Diagnosing Achilles tendonitis typically involves a thorough physical examination by a podiatrist or foot doctor, along with a review of the patient’s medical history and symptoms. In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be recommended to assess the extent of tendon damage and rule out other potential causes of heel pain.
Treatment for Achilles tendonitis focuses on relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and promoting healing. Common treatment options include:
- Rest and activity modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms and incorporating rest periods to allow the tendon to heal.
- Ice therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises: Performing specific stretching and strengthening exercises prescribed by a physical therapist or podiatrist to improve flexibility and support the Achilles tendon.
- Orthotic devices: Using orthotic inserts or heel cups to provide cushioning and support for the affected foot, reducing strain on the Achilles tendon.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter or prescription NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or naproxen may be recommended to alleviate pain and inflammation.
In severe cases of Achilles tendonitis where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, more advanced interventions such as corticosteroid injections, extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), or surgery may be considered.
Prevention of Achilles Tendonitis:
Preventing Achilles tendonitis involves adopting healthy habits and lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of overuse and injury. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Proper footwear: Wear supportive, well-fitting shoes appropriate for your activity level and foot type.
- Gradual training progression: Avoid sudden increases in training intensity or duration, and incorporate rest days into your exercise routine.
- Stretching and warm-up: Prioritize dynamic stretching and warm-up exercises before engaging in physical activity to prepare the muscles and tendons for movement.
- Strength training: Include strength training exercises that target the calf muscles, Achilles tendon, and surrounding muscles to improve stability and reduce the risk of injury.
- Cross-training: Incorporate low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling into your fitness regimen to reduce the repetitive strain on the Achilles tendon.
Conclusion:
Achilles tendonitis can be a painful and limiting condition, but with the right approach to treatment and prevention, it is often manageable and can be overcome. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Achilles tendonitis, individuals can take proactive steps to address the underlying factors contributing to their condition and regain mobility and comfort in their daily lives. If you’re experiencing symptoms of Achilles tendonitis, don’t hesitate to consult with a qualified podiatrist or foot doctor for personalized evaluation and treatment recommendations. Remember, early intervention and proactive management are key to achieving optimal outcomes and preventing long-term complications associated with Achilles tendonitis.
Stay informed, stay proactive, and take the necessary steps to keep your Achilles tendon healthy and resilient for years to come. Your feet will thank you for it!