Introduction to Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is a prevalent foot condition among runners, characterized by inflammation or irritation of the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon plays a crucial role in supporting the arch of the foot and stabilizing the ankle during walking and running.
Anatomy of the Posterior Tibial Tendon
The posterior tibial tendon runs along the inside of the ankle and foot, connecting the calf muscles to the bones on the inner side of the foot. Its primary function is to support the arch and facilitate foot movement.
Causes of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis often results from overuse or repetitive stress on the tendon. Factors such as excessive running, sudden increase in training intensity, improper footwear, and biomechanical abnormalities can contribute to its development.
Risk Factors for Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Runners who engage in activities with high impact or those who have flat feet, high arches, or excessive pronation are at a higher risk of developing posterior tibial tendonitis. Additionally, inadequate warm-up, poor conditioning, and tight calf muscles can increase the likelihood of injury.
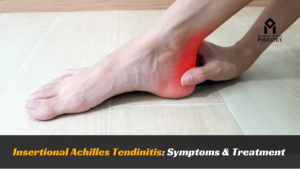
Signs and Symptoms of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Common symptoms include pain and swelling along the inside of the ankle and foot, especially with activity. Some individuals may experience difficulty walking or standing for prolonged periods due to the discomfort.
Diagnosis of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional, along with imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans to assess the extent of tendon damage.
Treatment Options for Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Conservative Management
Initial treatment often focuses on rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to reduce pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be prescribed to alleviate discomfort.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the tendon and improve flexibility. Stretching and strengthening routines tailored to individual needs can promote healing and prevent recurrence.
Orthotics
Custom orthotic inserts or supportive footwear can provide stability and relieve pressure on the affected tendon, aiding in the recovery process.
Medications
In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. However, these should be used judiciously due to potential side effects.
Surgical Interventions
For severe cases or when conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical repair of the posterior tibial tendon may be necessary to restore function and stability to the foot and ankle.
Prevention Strategies for Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
To prevent posterior tibial tendonitis, runners should:
- Gradually increase training intensity and mileage to avoid overuse injuries.
- Incorporate proper warm-up and cool-down routines before and after exercise.
- Wear appropriate footwear with adequate support and cushioning.
- Address any biomechanical abnormalities or gait issues through orthotic intervention.
- Listen to their bodies and rest when experiencing pain or discomfort.
- Rehabilitation and Recovery
- Rehabilitation for posterior tibial tendonitis focuses on restoring strength, flexibility, and function to the affected tendon and surrounding muscles. This may involve a combination of physical therapy, orthotic support, and gradual return to activity.
Importance of Rest and Recovery
Rest is essential for allowing the injured tendon to heal properly. Engaging in low-impact activities or cross-training during periods of rest can help maintain cardiovascular fitness without exacerbating the injury.
Returning to Running After Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Returning to running should be done gradually, starting with short distances and low intensity. As symptoms improve, runners can gradually increase mileage and intensity while monitoring for any signs of recurrence.
Incorporating Strength and Flexibility Exercises
Strength training exercises targeting the muscles of the lower leg and foot can help improve stability and prevent future injuries. Additionally, stretching exercises can enhance flexibility and range of motion.
Maintaining Good Footwear
Choosing appropriate footwear with adequate arch support and cushioning is essential for preventing overpronation and reducing stress on the posterior tibial tendon.
Listening to Your Body
It’s crucial for runners to pay attention to their bodies and recognize early warning signs of injury. Ignoring pain or pushing through discomfort can lead to more severe problems in the long run.
Conclusion
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is a common foot problem among runners, characterized by inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effectively managing the condition and preventing future injuries.
FAQs
Is posterior tibial tendonitis only common in runners?
While runners are at a higher risk due to the repetitive stress on the tendon, posterior tibial tendonitis can occur in individuals who engage in activities that involve excessive foot pronation or overuse of the tendon.
Can posterior tibial tendonitis be cured with rest alone?
Rest is an essential component of treatment, but in some cases, additional interventions such as physical therapy or orthotics may be necessary for complete recovery.
Are there any exercises to prevent posterior tibial tendonitis?
Strengthening exercises for the muscles of the lower leg and foot, as well as stretching routines to improve flexibility, can help prevent posterior tibial tendonitis by reducing stress on the tendon.
How long does it take to recover from posterior tibial tendonitis?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury and individual factors. With appropriate treatment and rehabilitation, most individuals can expect to return to running within a few weeks to several months.
What should I do if I experience persistent pain in my ankle or foot?
If you experience persistent pain or discomfort in your ankle or foot, it’s essential to seek evaluation from a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.