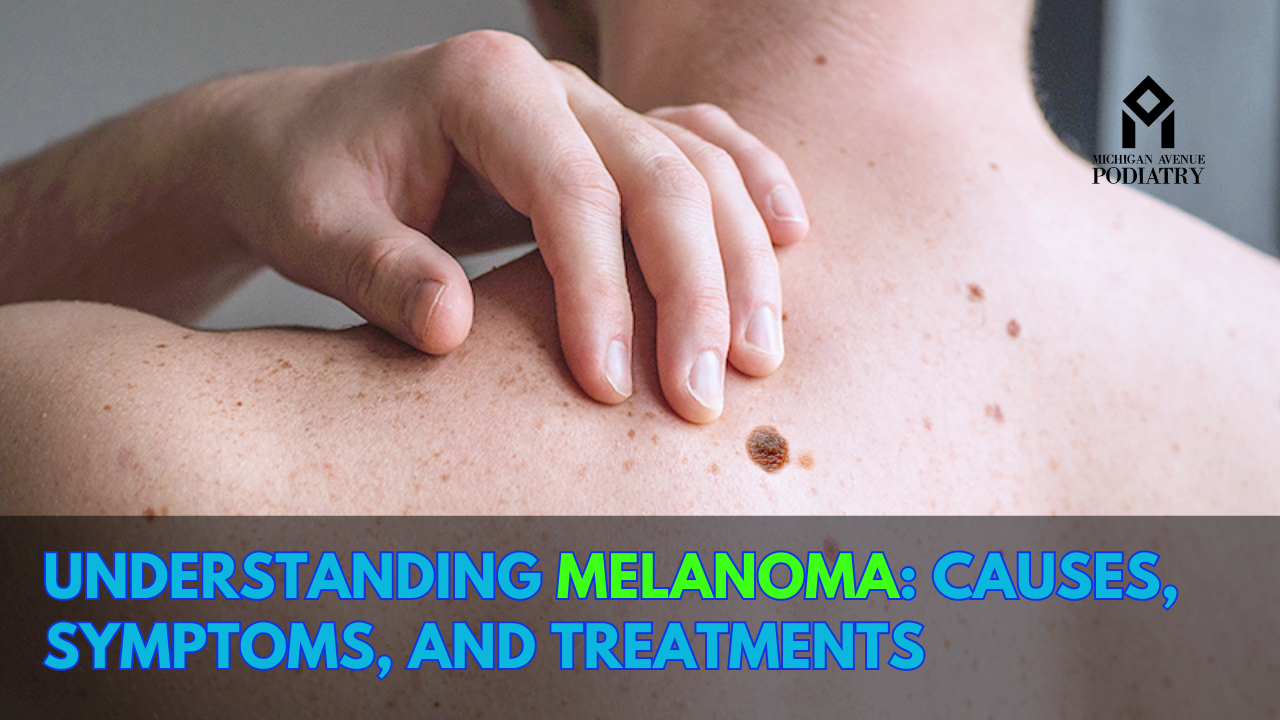
Melanoma, often referred to as melanoma cancer, is a type of skin cancer that originates in the melanocytes – the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. While melanoma is less common than other types of skin cancer, it is the most deadly. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking early treatment are crucial for effectively managing this condition. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of melanoma, including its causes, symptoms, and available treatments, with a particular focus on melanoma affecting the foot, requiring the expertise of podiatrists, or foot doctors.
Causes of Melanoma:
Several factors can contribute to the development of melanoma. One of the primary causes is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from the sun or artificial sources such as tanning beds. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can result in cancerous growths, including melanoma.
Other risk factors for melanoma include having fair skin, a history of sunburns, a family history of melanoma, having many moles or unusual moles, and a weakened immune system. While these factors increase the risk, melanoma can develop in individuals without any known risk factors, emphasizing the importance of regular skin checks and early detection.
Symptoms of Melanoma:
Detecting melanoma in its early stages significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. The ABCDE rule is a helpful guide for recognizing potential signs of melanoma:
A – Asymmetry: One half of the mole or lesion does not match the other half.
B – Border irregularity: The edges are irregular, notched, or blurred.
C – Color: The color is not uniform and may include shades of brown, black, or even pink, red, white, or blue.
D – Diameter: The size of the mole is larger than 6 millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser).
E – Evolution: The mole changes in size, shape, color, or texture over time.
In addition to the ABCDE rule, it’s essential to be aware of other warning signs, such as a mole or lesion that is itchy, painful, or bleeding, or the appearance of a new mole in adulthood.
Melanoma on the Foot:
While melanoma can occur anywhere on the body, including areas not exposed to the sun, it is less commonly associated with the feet. However, when melanoma does affect the foot, it can often go unnoticed or misdiagnosed due to its location and resemblance to other benign conditions, such as moles or bruises.
Podiatrists play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating melanoma affecting the foot. Their specialized knowledge of foot anatomy and conditions enables them to recognize suspicious lesions and conduct thorough examinations. Patients should not overlook any unusual growths or changes in existing moles on their feet and seek prompt evaluation by a podiatrist if concerns arise.
Treatments for Melanoma:
The treatment approach for melanoma depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, its location, and the individual’s overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for melanoma involves surgically removing the cancerous growth and a margin of healthy tissue surrounding it. In cases where melanoma has spread beyond the skin, surgery may also involve removing nearby lymph nodes.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy works by stimulating the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. This approach has shown promising results in treating advanced melanoma and may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy drugs are designed to interfere with specific molecules involved in cancer growth. These drugs are prescribed based on the presence of specific genetic mutations in the melanoma cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells. It may be recommended as a primary treatment for melanoma in certain cases or used after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Conclusion:
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that requires early detection and prompt treatment for the best outcomes. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can improve their chances of successful treatment and long-term survival. Additionally, individuals should not overlook the importance of regular skin checks, including thorough examinations of the feet, with the assistance of podiatrists or foot doctors, to detect melanoma in its early stages. With advancements in treatment options and multidisciplinary care, the prognosis for melanoma patients continues to improve, offering hope for a brighter future.