Foot fungus, medically termed tinea pedis, encompasses various types of fungal infections affecting the feet. These infections are commonly found in warm and moist environments, such as sweaty shoes or communal shower floors. Recognizing the different types of foot fungus is crucial for effective management and prevention. Here, we delve into the nuances of each type, along with practical tips for treatment and prevention.
Common Types of Foot Fungus
- Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis)
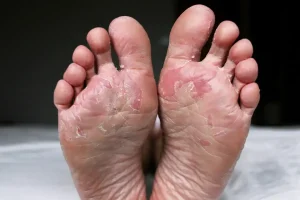
- Athlete’s foot is perhaps the most prevalent type of foot fungus, characterized by itching, burning, and cracked, peeling skin, primarily between the toes. It thrives in warm and damp environments, making it common among athletes and individuals who wear tight-fitting shoes for extended periods.
- Toenail Fungus (Onychomycosis)
- Onychomycosis affects the toenails, causing them to become discolored, thickened, and brittle. This type of foot fungus often starts at the edge of the nail and gradually spreads, leading to pain and discomfort. It can result from untreated athlete’s foot or direct exposure to fungi.
- Ringworm of the Foot (Tinea Corporis)
- Ringworm of the foot, also known as tinea corporis, presents as red, scaly patches on the soles, sides, or top of the feet. Despite its name, it is not caused by worms but rather by dermatophyte fungi. This type of foot fungus is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with infected skin or surfaces.
Treatment and Prevention
Effective management of foot fungus involves a combination of topical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and proper foot hygiene. Here are some key strategies:
- Antifungal Medications: Over-the-counter antifungal creams, sprays, or powders can help alleviate symptoms and eradicate the fungus. In severe cases, prescription medications may be necessary.
- Keep Feet Clean and Dry: Regularly wash and thoroughly dry your feet, paying close attention to the spaces between the toes. Avoid wearing damp socks or shoes for prolonged periods.
- Wear Breathable Footwear: Opt for shoes made of breathable materials, such as leather or mesh, to promote airflow and reduce moisture buildup.
- Use Foot Protection in Public Areas: Wear flip-flops or sandals in communal showers, locker rooms, and swimming pool areas to minimize direct contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Practice Good Foot Care: Trim toenails straight across and avoid cutting them too short to prevent ingrown toenails, which can create an entry point for fungal infections.
Conclusion
Different types of foot fungus pose varying degrees of discomfort and inconvenience, but with proper understanding and proactive measures, they can be effectively managed and prevented. By incorporating good foot hygiene practices, wearing breathable footwear, and seeking timely treatment when necessary, individuals can maintain healthy and fungus-free feet.



Its like you read my mind! You appear to know so much about this, like yoou wrot the book in it or something.
I think that you coyld do with a few pics to drive the message home a bit, but ogher than that, this is magnificent blog.
A fantastic read. I’ll certainly be back.